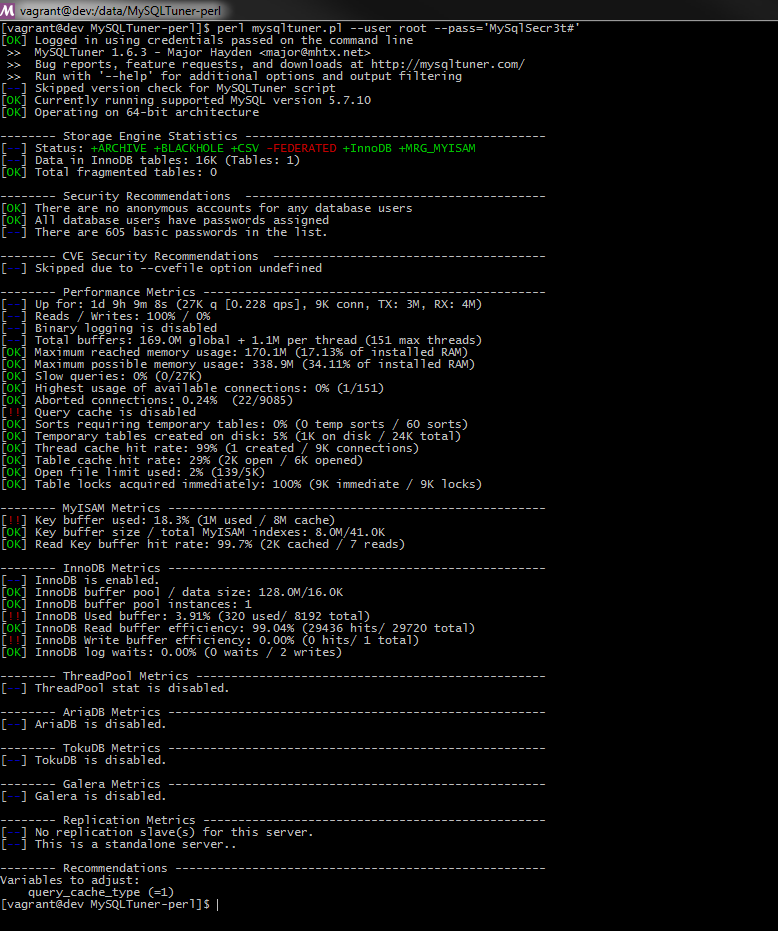
ThinkPHP3.2 UEditor 添加在线管理图片删除功能
第一,需要添加一个 php 文件来实现删除功能,文件添加到:ueditor\php\action_delete.php 代码内容:
<?php
/*---------------------------
* Flyヽ
* http://lfei.org
* 2016-02-04
* action_delete.php
* 删除 Ueditor 目录下的文件
*---------------------------*/
try {
//获取路径
$path = $_POST['path'];
$path = str_replace('../', '', $path);
$path = str_replace('/', '\\', $path);
//安全判断(只允许删除 ueditor 目录下的文件)
if(stripos($path, '\\ueditor\\') !== 0)
{
return '非法删除';
}
//获取完整路径
$path = $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT'].$path;
if(file_exists($path)) {
//删除文件
unlink($path);
return 'ok';
} else {
return '删除失败,未找到'.$path;
}
} catch (Exception $e) {
return '删除异常:'.$e->getMessage();
}第二,需要在ueditor\php\controller.php文件的switch中添加命令 deleteimage 的处理:
....
switch ($action) {
....
/* 删除图片命令处理 */
case 'deleteimage':
$result = include('action_delete.php');
break;
/* 在 default 之前添加 */
default:
$result = json_encode(array(
'state'=> '请求地址出错'
));
break;
}
....第三,在图片上添加删除按钮,需要修改 Js 文件:ueditor\dialogs\image\image.js
....
/* 在这两句之后添加 */
item.appendChild(img);
item.appendChild(icon);
/* 添加删除功能 */
item.appendChild($("<span class='delbtn' url='" + list[i].url + "'>✖</span>").click(function() {
var del = $(this);
try{
window.event.cancelBubble = true; //停止冒泡
window.event.returnValue = false; //阻止事件的默认行为
window.event.preventDefault(); //取消事件的默认行为
window.event.stopPropagation(); //阻止事件的传播
} finally {
if(!confirm("确定要删除吗?")) return;
$.post(editor.getOpt("serverUrl") + "?action=deleteimage", { "path": del.attr("url") }, function(result) {
if (result == "ok") del.parent().remove();
else alert(result);
});
}
})[0]);
/* 在这一句之前添加 */
this.list.insertBefore(item, this.clearFloat);
....第四,为删除按钮添加一个样式,修改文件:ueditor\dialogs\image\image.css在最底部添加如下代码:
/* 在线管理删除按钮样式 */
#online li .delbtn {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 0;
border: 0;
z-index: 3;
color: #ffffff;
display: inline;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 10.5px;
padding:3px 5px;
text-align: center;
background-color: #d9534f;
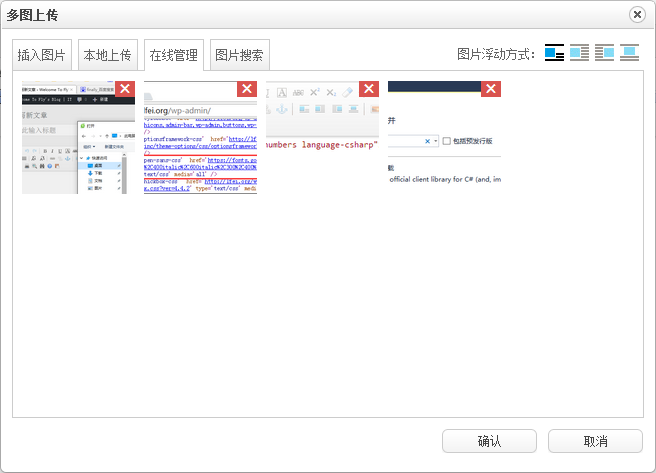
}效果如下:
转自:http://lfei.org/ueditor-manage-image-delete/